Explained: How cars can run on hydrogen
Why in news?
Ahead of next July’s Tokyo Olympics, Japan is gearing up to put on its roads thousands of vehicles based on a hydrogen cell technology, also known as ‘fuel cells’.
How it works?
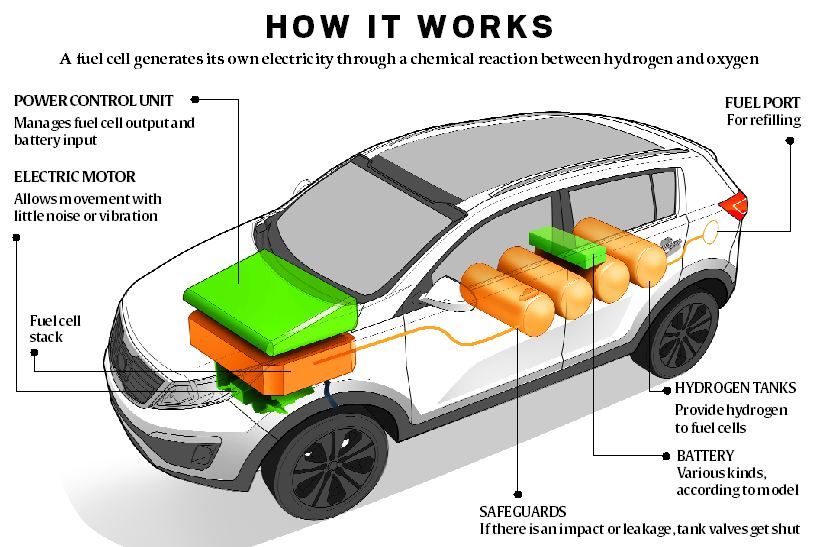
Fuel used: Hydrogen + Oxidant
Process: Produced electricity by an electrochemical process
Fuel cell combines hydrogen and oxygen to generate an electric current, water being the only byproduct. It converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
So is an FCEV a conventional vehicle or an electric vehicle (EV)?
While the fuel cells generate electricity through an electrochemical process, unlike a battery-electricity vehicle, it does not store energy and, instead, relies on a constant supply of fuel and oxygen — in the same way that an internal combustion engine relies on a constant supply of petrol or diesel, and oxygen. In that sense, it may be seen as being similar to a conventional internal combustion engine.
Difference is :
But unlike the combustion engine cars, there are no moving parts in the fuel cell, so they are more efficient and reliable by comparison. Also, there is no combustion onboard, in the conventional sense.
Electric Vehicles (Evs) classification:
- Battery electric vehicle or BEVs such as the Nissan Leaf or Tesla Model S, which have no internal combustion engine or fuel tank, and run on a fully electric drivetrain powered by rechargeable batteries.
- Conventional hybrid electric vehicles or HEVs such as the Toyota Camry sold in the country combine a conventional internal combustion engine system with an electric propulsion system, resulting in a hybrid vehicle drivetrain that substantially reduces fuel use. The onboard battery in a conventional hybrid is charged when the IC engine is powering the drivetrain.
- Plug-in hybrid vehicles or PHEVs, such as the Chevrolet Volt, too have a hybrid drivetrain that uses both an internal combustion engine and electric power for motive power, backed by rechargeable batteries that can be plugged into a power source.
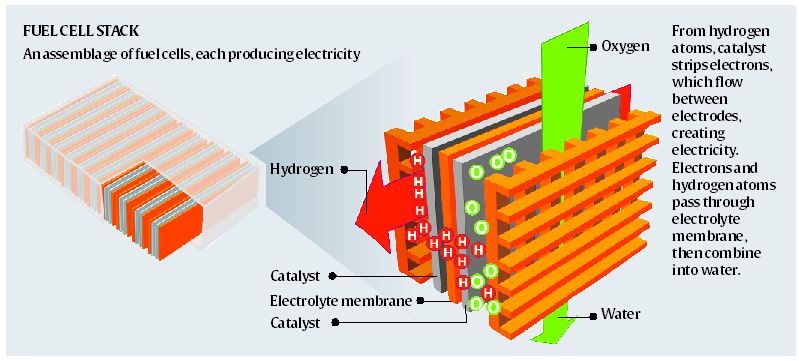
FCEVs are widely considered to be the next frontier in EV technology. FCEVs such as Toyota’s Mirai and Honda’s Clarity use hydrogen to power an onboard electric motor. Since they are powered entirely by electricity, FCEVs are considered EVs — but unlike BEVs, their range and refuelling processes are comparable to conventional cars and trucks.
Advantages and disadvantages of fuel cells
- Fuel cells produce much smaller quantities of greenhouse gases and none of the air pollutants that cause health problems.
- Also, if pure hydrogen is used, fuel cells emit only heat and water as a byproduct. Such cells are also far more energy-efficient than traditional combustion technologies.
- Unlike battery-powered electric vehicles, fuel cell vehicles do not need to be plugged in, and most models exceed 300 km of range on a full tank. They are filled up with a nozzle, just like in a petrol or diesel station.
Disadvantages/challenges of Fuel Cells operated Vehicles
- While FCEVs do not generate gases that contribute to global warming, the process of making hydrogen needs energy — often from fossil fuel sources.
- Also, there are questions of safety — hydrogen is more explosive than petrol.
- Opponents of the technology cite the case of the hydrogen-filled Hindenburg airship in 1937.
- The other major hurdle is that the vehicles are expensive, and fuel dispensing pumps are scarce.
Progress in India
- In India, so far, the definition of EV only covers BEVs; the government has lowered taxes to 12%.
- At 43%, hybrid electric vehicles and hydrogen FCEVs attract the same tax as IC vehicles.
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy has been supporting various such projects in academic institutions, research and development organisations and industry for development.
- The Ministry of Science and Technology has supported two networked centres on hydrogen storage led by IIT Bombay and Nonferrous Materials Technology Development Centre, Hyderabad.
Thank you!
